How Does Sexual Selection Explain Differences in Males and Females
Selection preferences in males Like their female counterparts males also use visual information about a potential mate as well as voice body shape and an assortment of other factors in selecting a partner. In birds the first form of sexual selection occurs when males compete for territories as is obvious when those territories are on leks traditional mating grounds.

Males Are The Taller Sex Estrogen Not Fights For Mates May Be Why Quanta Magazine
Provide examples of each 1 males may provide more parental care than females phalaropes have high next predation so females must compete for males who will incubate and rear the offspring females are polyandrous brightly colored and territorial 2 females are polyandrous.
. Humans are sexually dimorphic. There are many reasons for this. The more competitive and aggressive sex is usually the male particularly in.
Age at sexual maturation is one of the most important life-history traits of organisms because it greatly affects fitness by influencing the number of reproductive opportunities and survival Roff 2002 and consequently mating success in males and fecundity in females Stearns and Koella 1986Therefore individuals are expected to mature at the point. The second kind of sexual selection accounts for the fighting structures and behaviors observed in many animal species typically within the male sex. Females select males using factors including voice pitch facial shape muscularity and height.
This fundamental difference in gamete size or anisogamy predisposes the sexes to different reproductive organs which are termed primary sexual characters. A When males are subject to stronger sexual selection than females males will evolve secondary sexual characters that result in marked differences between the sexes. How does sexual selection explain differences between males and females and their behaviors.
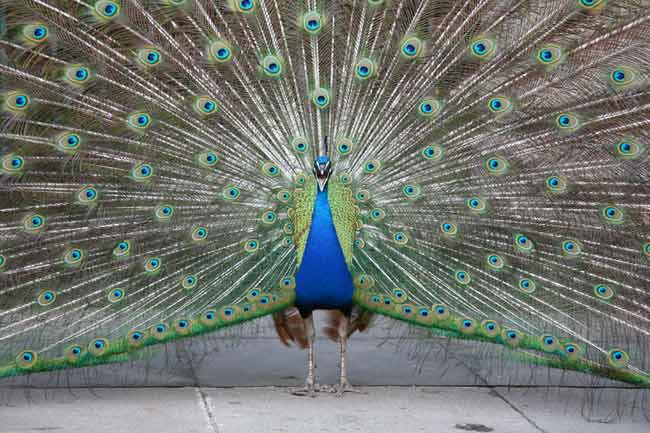
Darwin proposed that these characteristics were the result of a secondary mechanism operating alongside natural selection - a mechanism he called sexual selection. It is a mechanism of two parts involving physical adaptation in males but also aesthetic sense in females who in many cases played a crucial role in selecting males. Larger body size in males than in females greater muscle mass and structures such as antlers are explained as adaptations for male-male competition evolved via sexual selection.
Sexual selection can lead to males having much more extravagant colors or behaviors these both are worse for the survival of the animal but ultimately are still selected for because they lead to the male mating more. The female will play an active role in choosing her mate and will choose the mate with the best characteristics in order to produce the offspring with the best characteristics. There are 2 types of sexual selection.
Intersexual selection takes place when males compete for the attention of a female. Sex differences in sexual selection often coincide with contrasting mating interests or optimal phenotypes of males and females ie. This is referred to as anisogamy.
The traditional and enduring textbook explanation for sex differences in hominid body size is sexual selectionwith large ancestral males winning competitions which boosted their reproductive success compared to smaller males. Unlike in the natural selection there are terms called male choice and female choice in the sexual selection. The other type is Intrasexual selection.
Conversely the sex that is chosen is also the sex that fights with members of the same sex for access to mates and is traditionally the one that invests less in gamete production. Peacocks do not provide any. Gamete production and investment is.
Sexual selection applied to human aggression Because gestation in female mammals is internal males must show a higher potential reproductive rate than females and this is associated with being the competitive sex. Sexual selection involves the choice of members of one sex by the other and competition by members of one sex for access to the other Darwin 18711901. In many species females produce just a few large and costly eggs while males produce many small and less expensive sperm.
By definition males and females differ in the size of their gametes. Principles of sexual selection. In some species of grouse and other such birds.
Both sexual selection and sexual conflict are potent forces driving trait evolution. The difference in gamete size and number can explain why females are choosy about which males to mate with. What are two causes of sexual selection in females.
The strength of sexual selection ranged from intense competition and choice where 90 males competed for reproduction with only 10 females through to the complete absence of sexual selection with. Research shows that males tend to prefer feminine womens faces and voices as opposed to women with masculine features in these categories. It would lead to greater variation in sexually selected traits among males than among females.
The strength of sexual selection ranged from intense competition and choice where 90 males competed for reproduction with only 10 females through to the complete absence of sexual selection with. The characteristics which have been arisen from sexual selection may be useless except for mating purposes but the characteristics that have been arisen from natural selection result usually in new adaptations in individuals. The differences in fecundity between females generated by intrasexual competition for resources may commonly lead to large individual differences in fecundity Clutton-Brock et al 1982 Clutton-Brock et al 1988 Owens and Thompson 1994 which are likely to strengthen selection on males to identify and prefer superior partners and on.
Sexual selection as an explanatory framework for human aggression 211. Generally it is unusual for males to be choosy about their mates. Males make many small sperm whereas females make fewer and larger eggs.
Among the many instances of sexual selection in mammals is extreme sexual dimorphism with males as much as six times heavier than females and male fighting for dominance among elephant seals. Males that manage to acquire the best territories on a lek the dominant males are known to get more chances to mate with females. Many male traits are well explained by sexual selection theory as adaptations to mating competition and mate choice whereas no unifying theory explains traits expressed more in.
Eeob 400 Lecture 9 Sexual Selection Ppt Video Online Download
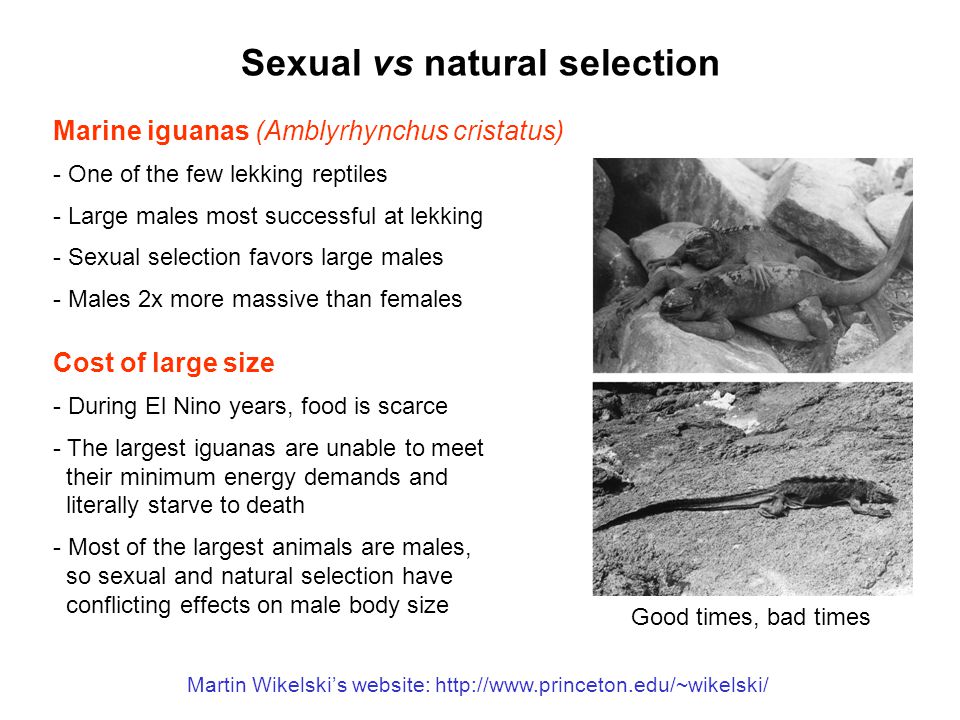
Eeob 400 Lecture 9 Sexual Selection Ppt Video Online Download

Eeob 400 Lecture 9 Sexual Selection Ppt Video Online Download

Males And Females Often Look Different Ppt Download

Males And Females Often Look Different Ppt Download

Sexual Selection Explained Evolution 101 Youtube

Sexual Selection And Mate Choice Lab Bio Jove

Sexual Selection Definition Forms Study Com

Male Female The Evolution Of Human Sex Differences Apa Publishing Apa

Sexual Selection Biology Britannica

Why Is Sexual Selection So Powerful Understanding Evolution

Difference Between Intrasexual And Intersexual Selection Compare The Difference Between Similar Terms

Sexual Selection An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

Sexual Dimorphism An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

How Peacocks Got Their Colorful Tails Live Science

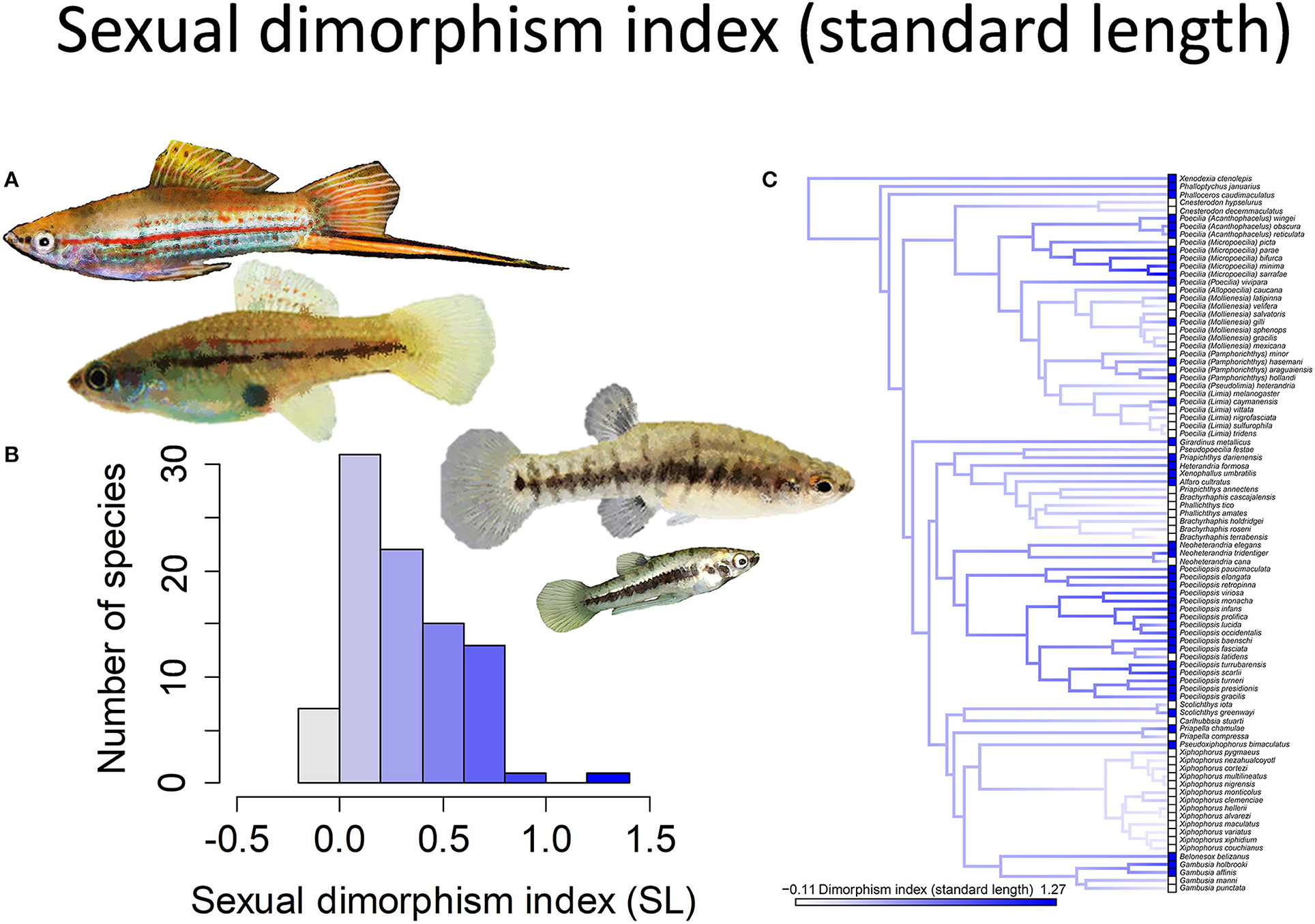
Frontiers Reproductive Mode And Conflict Shape The Evolution Of Male Attributes And Rate Of Speciation In The Fish Family Poeciliidae Ecology And Evolution

Sex Differences In Age To Maturation Relate To Sexual Selection And Adult Sex Ratios In Birds Ancona 2020 Evolution Letters Wiley Online Library
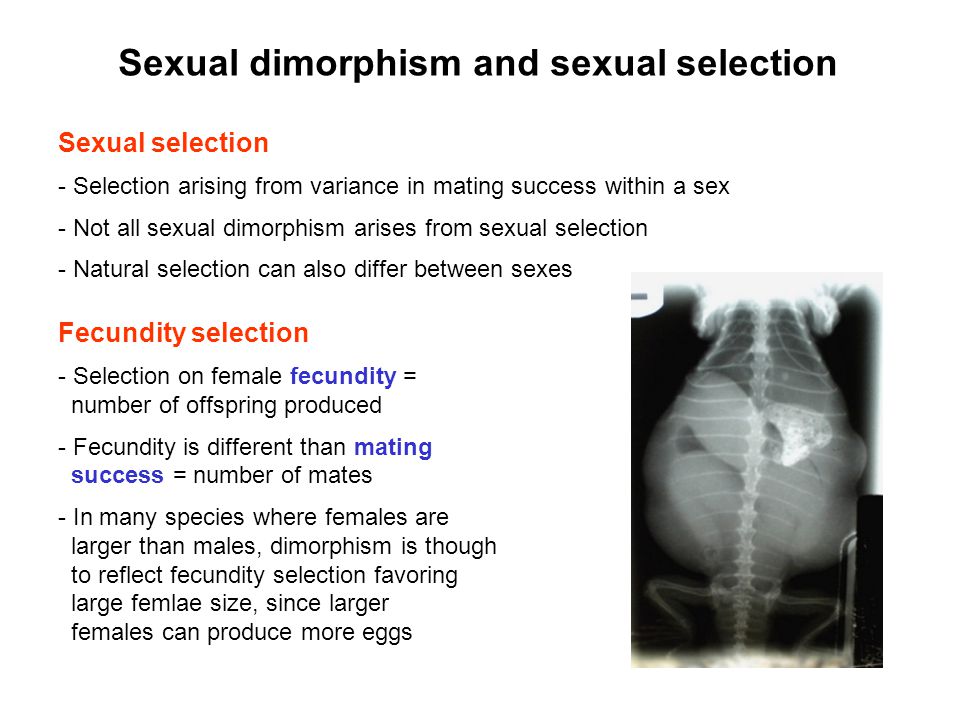
Eeob 400 Lecture 9 Sexual Selection Ppt Video Online Download

Comments
Post a Comment